Green building ideology has been steadily increasing since the 1970s. This architectural philosophy aims to create an environmentally friendly structure. It’s an ecological standard that should be maintained throughout its entire existence. Green building minimizes negative environmental impact, preserves raw materials, and provides a healthy indoor atmosphere. Green homes are often referred to as sustainable or eco-homes.

From residential structures to corporate facilities, architects are discovering new sustainable design processes to preserve our ecosystem while reducing our carbon footprint. Here are ten benefits of sustainable green building and green construction practices and how this architectural trend can protect the generations of tomorrow:
Reduce Carbon Footprint
Global warming caused by carbon emissions is a serious issue. Major initiatives are underway in almost every country to reduce the world’s carbon footprint. There has been an increase in large corporations opting for green initiatives. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), buildings account for 30% of all greenhouse gas emissions in the United States. The construction industry can make an enormous impact on reducing carbon emissions. It has been estimated that green building can significantly reduce carbon emissions by at least 50% before the middle of the twenty-first century. Simply by choosing sustainable materials and installing ecological systems, an American home awarded LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification can reduce its carbon footprint by at least 25%.
Efficient & Sustainable Materials
Architects and interior designers are being creative with their choice of materials. Recycling and upcycling components from existing structures save raw materials from being taken from the environment. It also reduces energy levels by reducing the burden on manufacturing building supplies such as roof tiles and bricks. By using recycled material and reusing resources (and even repurposing old structures), sustainable architects, engineers, and green designers are tapping into existing resources to reduce carbon footprints and save natural resources. By implementing sustainable strategies into the design process, like reducing waste, preserving natural resources (such as water and wood), protecting our air supply, and limiting energy use, green building companies can create extremely efficient structures that can withstand the test of time. Design trends such as minimalism help to keep buildings stylishly sleek. Upcycling can be as simple as using driftwood for shelving. Recycling materials prevents valuable commodities from being sent to landfill sites.
Saving Water: Reduce, Reuse, Replenish
Water is one of the most valuable commodities on earth. Research shows that green architecture can not only reduce water waste through water-efficient plumbing fixtures but also reduce the strain on shared water resources. Using ecological plumbing systems is a crucial element. Installations such as rainwater and gray water catchment systems can effectively recycle wastewater for flushing toilets. Innovative composting toilets don’t even use water. Other fittings might include showerheads with low flow output. Hot water systems that are based on point-of-use heating contribute significantly to reducing energy and water resources. Buildings only need to reach an 11% reduction in water usage to qualify for LEED accreditation, but a green building can save up to 30%.
Solar Energy
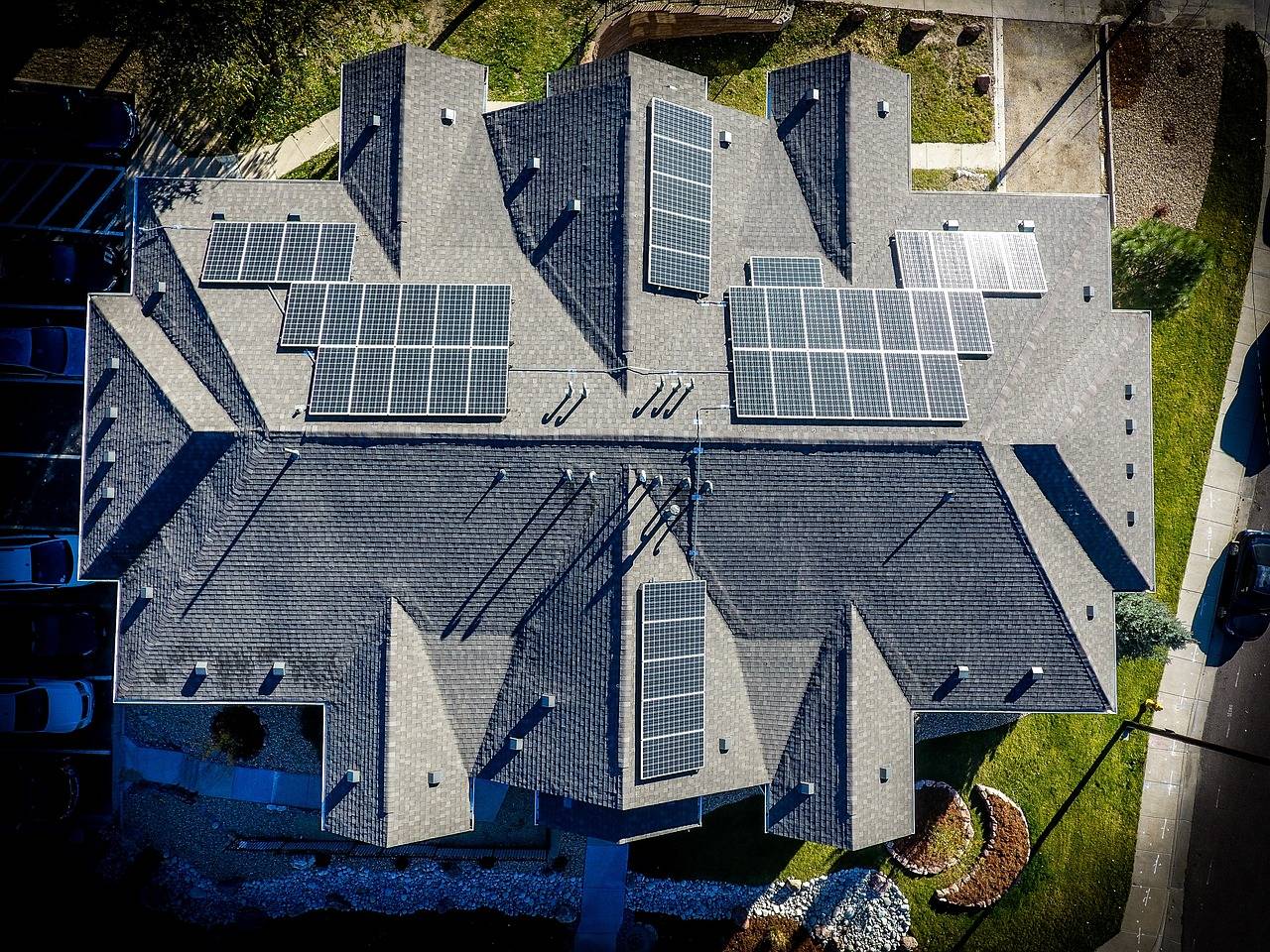
Green buildings focus on using natural energy sources for electricity. The use of solar power in the US increased by 23.1% in 2020. However, it still only represents around 3.3% of the entire national output. Using solar energy in a green building helps to increase independence from grid-generated electricity. Solar photovoltaic panels absorb natural energy from the sun and convert it to usable electricity. It can even be stored in batteries for use during hours of darkness. Solar power is a sustainable commodity that is freely available. Installing a solar energy system in a green building reduces household expenditure and carbon emissions.
Energy-Efficient
As a green architect, energy efficiency is a primary goal in green building design. Developing structures that derive their energy from natural sources – such as the sun, wind, and water – is extremely beneficial to the environment, protecting the ecosystem from pollution associated with non-renewable sources (such as oil and coal). An added benefit: non-renewable energy sources are not only toxic but costly. In fact, their energy-efficient counterparts (such as solar energy vs. traditional electricity) can save thousands over the lifetime costs of the infrastructure.
Indoor Air Quality
When it comes to our quality of life, it’s no secret that our surroundings have a major impact on our health. A green building aims to improve indoor air quality. Greater attention is paid to natural ventilation systems. The simplest way to provide fresh air in a green building is through its windows. They can be oriented to maximize the air currents in the local surroundings. SMART ventilation systems ensure window apertures are always set at an optimal level. Convection cooling systems draw fresh air in and release it once it has absorbed excess heat. Occupants residing or working in green structures have experienced a marked improvement in their health, stress levels and overall quality of life.
Enhanced Health: Eco-Friendly For Life
Green buildings are designed to be healthy. Living in a sustainable building can save your life – literally. According to studies, people who reside in green structures experience a myriad of health benefits due to the eco-friendly materials utilized in construction. Green buildings avoid using building materials that may contain harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or plastic by-products. These by-products have been known to release toxic fumes and carcinogens into the atmosphere. Timber products won’t have been treated with sealants containing formaldehyde. Some plastic is biodegradable, but other forms can be recycled for use in the construction industry. It benefits the health of a green building by inhibiting the growth of harmful allergens such as mold, fungi, and bacteria. Combined with efficient ventilation systems, the green building should achieve a superior, healthy indoor environment. These dangerous materials are linked to respiratory disease, allergies, and other health disorders, and in extreme cases, an increased risk of cancer.
Reduced Operational Cost and Maintenance
One of the greatest benefits of green buildings are their lower maintenance costs – featuring specially-engineered design elements to lower energy consumption and help reduce energy cost and water bills for each occupant. These efficient structures can save corporate and residential owners a bundle. Although the expense required for building owners to build such structures may be initially higher than traditional non-green forms of architecture, the cost over the long term is recovered exponentially.
Increased Value
Green buildings can sometimes be more expensive to construct. This is due to the additional, innovative features. Advanced SMART plumbing and heating systems contribute to the cost. But the maintenance of a green building is generally much less than a conventional building. On average, a green building realizes an increase of 7% in real estate valuations.
Durability – Built To Last
For educated homeowners, going green is a no-brainer: from energy and water savings and improved air quality to overall durability, sustainable materials have been proven time and time again to last longer. Green materials (such as recycled decking and roofing) not only endure for years exposed to the elements but require much less maintenance. In addition, because many of them are free from harmful chemical treatments, they are healthier for the environment (and the inhabitants they serve).